On September 16, 2014, Governor Jerry Brown signed three bills into law: Assembly Bill 1739, Senate Bill 1319, and Senate Bill 1168, that became collectively known as the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA), creating a framework for sustainable, local groundwater management for the first time in California history. In 2015, the California Department of Water Resources (DWR) evaluated and prioritized the 515 groundwater basins identified in DWR Bulletin 118, and 127 of these groundwater basins were designated as high- or medium-priority basins requiring them to be sustainably managed by 2042. SGMA required local authorities to form Groundwater Sustainability Agencies (GSAs) by June 30, 2017, to evaluate conditions in their local groundwater basins and adopt locally-based Groundwater Sustainability Plans (GSPs), or Alternative GSPs, tailored to their regional economic and environmental needs by January 1, 2020, for critically over-drafted basins, and January 1, 2022, for the remaining high- and medium-priority basins.
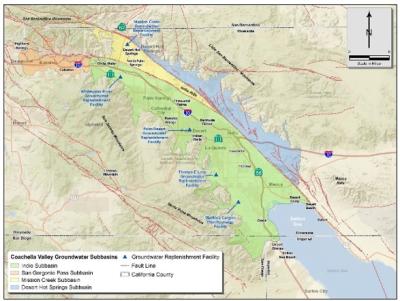
Coachella Valley Groundwater Basin and Subbasins
The Coachella Valley Groundwater Basin has been divided into four subbasins as defined in DWR Bulletin 118:
- Indio Subbasin (7-21.01)
- Mission Creek Subbasin (7-21.02)
- San Gorgonio Pass Subbasin (7-21.03)
- Desert Hot Springs Subbasin (7-21.04)
The Indio, Mission Creek, and San Gorgonio Pass Subbasins have been designated as medium-priority, and the Desert Hot Springs Subbasin has been designated as very low-priority, by the DWR.
Mission Springs Water District (MSWD) is actively participating in the implementation of SGMA in the Mission Creek and San Gorgonio Pass Subbasins. More information regarding SGMA compliance is available using the links below.
